How To Read A Histogram -camera
 What is a Histogram
What is a Histogram
A Histogram is a Quality Control Tool that graphically displays a data set.
More specifically, a Histogram is a type of Bar Chart that graphs the frequency of occurrence of continuous data, and will assistance y'all in analyzing your data.
Why would yous want to graphically display data?
Because every bit a Quality Engineer you lot probably already sympathise that every process, product or service has variation.
Which means that every slice of information that you collect will take variation in information technology, and this variation will be in a "Blueprint".
And the all-time way to see or understand this Pattern of variation is to graph your data using a Histogram.
In that style, the pattern of the variation inside the data volition become obvious! More on Distributions below.
Difference between a Bar Chart & Histogram
I said above that the Histogram is a blazon of Bar Nautical chart because they both use vertical bins to brandish information.
Yet there is a singled-out deviation between a Histogram and Bar Chart, and yous need to know which i to employ depending on the information assay that yous're trying to perform.
A Histogram volition group your data into Bins or Ranges while a bar chart displays discrete information past categories.
If your data is discrete or in Categories, so y'all should use a Bar chart instead of a Histogram.
Creating a Histogram
So – y'all've got some data and you'd like to create a Histogram to study the design of variation – Keen!
Below are the three steps you lot must go through to create a powerful Histogram.
 Step 1 – Minimum Data Points
Step 1 – Minimum Data Points
To accurately analyze a information fix, it'due south commonly recommended that yous have at to the lowest degree 50 data points. Without an adequate amount of data, you cannot make reasonable conclusions about your information.
Basically y'all may miss the pattern in the variation.
On the flip side of this requirement, one of the strengths of the Histogram is that it allows you lot to hands clarify large information sets, so don't experience shy most collecting or analyzing ALOT of data.
Step 2 – Number of Bins
Now that you've collected an acceptable amount of data, information technology's time to calculate the number of Bars, sometimes chosen Bins or Ranges, for your data set. The number of Bars for your Histogram will depend on the number of data points you collected.
Selecting the right number of Bins is of import as information technology tin can drastically affect the appearance of your data, which might atomic number 82 you lot to the wrong conclusion.
Below is a table from The Quality Toolbox that you lot tin reference when selecting the proper number of Bars. I too accept to notation that I've seen other people just take the Square Root of the full information size to go the number of Bins.
 Step 3 – Make up one's mind Bin Width
Step 3 – Make up one's mind Bin Width
Once yous've determined the number of Bins for your Histogram, it's time to calculate the Width or Range of each individual Bin.
To do that yous take the unabridged Range of the data (Max information point minus Min information point) and divide by the total number of Bins.
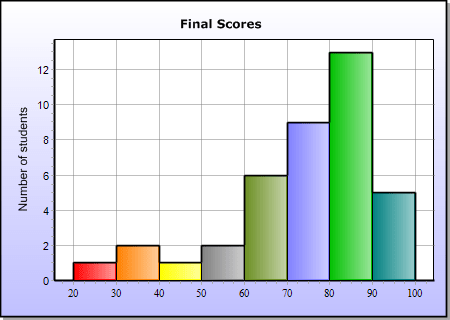
So for example, permit's say you're creating a Histogram of Student's Exam Scores on an exam and the maximum score was 100 and the minimum score was 20; then your Range is 80(100 – 20).
And so you tin divide your data Range (lxxx), by the total number of Bins, lets say eight in this instance. So the Width of each Bin is 80/ 8 = ten.
Similar to selecting the right number of total Bins, it's important that you continue all the Bin widths the aforementioned or this will skew the distribution of the information.
Resources & Videos for Histogram Creation
Here's a nifty resource from ASQ that will assistance you summate the correct number of Bins & the Width of each Bin for your Histogram.
Here's an interesting Resources from Shodor.org. They put together an Interactive Histogram that shows you how a Histogram changes when you lot play with the Width or Interval of each Bin.
Hither'southward a adept YouTube video that explains the bones method of amalgam a Histogram by paw. Information technology's a bit deadening for my gustatory modality, but information technology walks you (slowly) through the entire procedure!
Here's another video from Khan University.com that walks you through the creation of a Histogram.
Create a Histogram in Excel
And then, the above instructions are how to create a manual Histogram graph, which you must know and empathise for the CQE Examination.
Merely who's going to be creating a Histogram on newspaper now-a-days??? Then I wanted to include a YouTube video on how to create a Histogram in Excel 2010. If you're already using Excel 2013, I've added a separate link in the External Resources section beneath.
You lot should still empathise the nuts above regarding the correct number of Bins & Bin Width when using Excel.
Histogram Distributions
Now that you've created your histogram, it's time to analyze the pattern of variation. To do this you must understand the unlike Distribution types & what they each imply about your process.
The 4 most common Distributions are:
- Normal Distribution
- Double-Peaked (Bi-Modal) Distribution
- Plateaued (Multimodal) Distribution
- Skewed Distribution
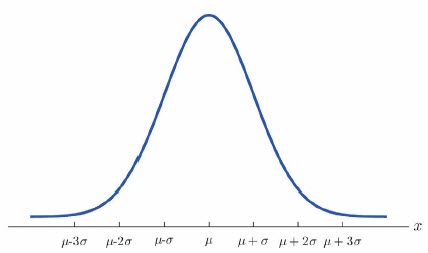
The Normal Distribution
Below is an example of the Normal Distribution, in this distribution your information is evenly distributed and centered effectually your Mean value.
This type of distribution can often exist interpreted that there is ane principal source of variation that drives this distribution, yet there can always exist other smaller sources of variation that contribute to the full variation.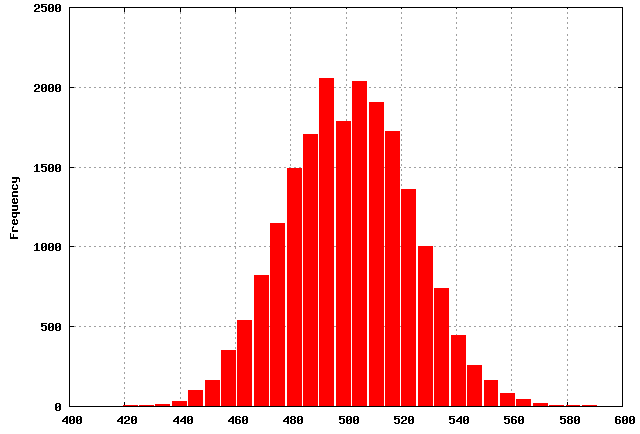
The Bi-Modal Distribution
Belwo is an example of the Bi-Modal Distribution. For Processes that brandish this distribution, it is ordinarily understood that there are 2 independent sources of Variation that result in Peaks within the data.
Or, as in the data below, the data can reveal a shift in the procedure. Hither's an interesting article from StatCrunch.com about the Kentucky Derby. Spoiler alert, they shortened the race in the late 1800's. 
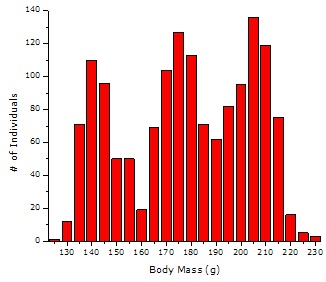
Multi-Modal Distribution
Below is an example of the Multi-Modal Distribution. When a process displays this pattern of variation it more often than not means that at that place are multiple sources of variation that are affecting the event.
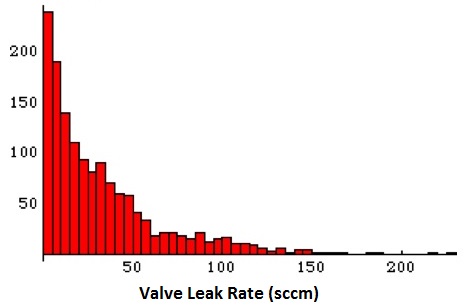
Skewed Distribution
Below is an example of a Skewed Distribution. Skewed Distributions can exist skewed in either the Left or Right direction.
A Skewed Distribution is normally the result of measurements or processes that have a natural limit.
For case if y'all were measuring the air leak on a valve, the natural limit would exist nix. You tin't take a non-zero leak rate, and nearly of your data points (if your process was practiced) would be near zero. Then this leak rate might trail off to large, infrequent leak rates.
Here's a good YouTube Video that walks through many of the Histogram Distributions and their common interpretations.
Power of a Histogram
As I said above, the Histogram is a powerful tool, and so I wanted to provide you with some examples of the type of analysis you tin perform with a Histogram.
Beneath I've covered 4 situations you lot may encounter where a Histogram would exist very powerful (simply you're not limited as well only these situations!):
- Determining the Design of Variation in back up of Continuous Improvement
- Determining if a Product or Service is reliably hit a Design Criteria
- Measuring a Process Comeback or Changes in a process
- Comparing the variation of two Like Processes
Design of Variation & Continuous Comeback
The commencement Powerful feature of a Histogram, equally I said above, is that it will allow you to see the pattern of variation within your data
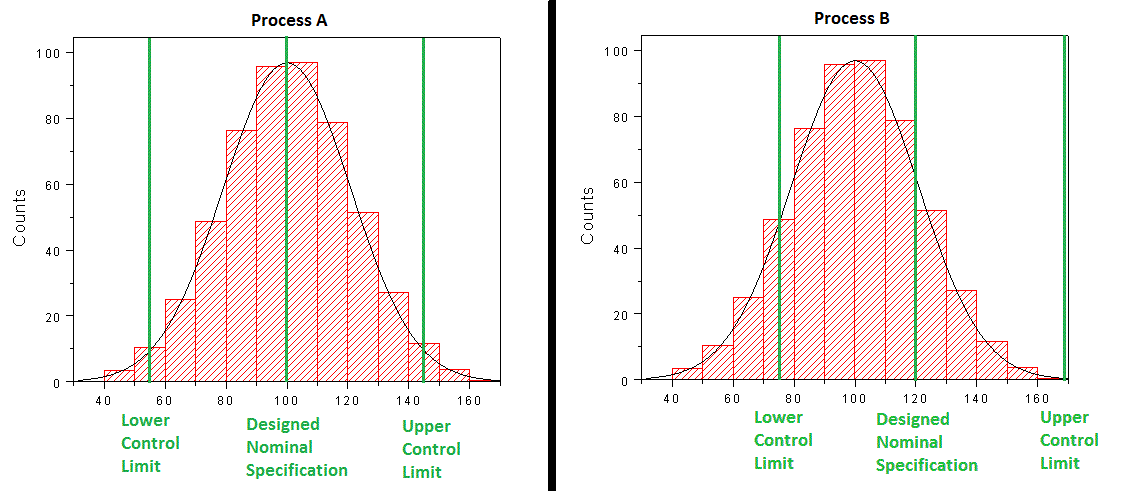
So permit's say that you lot've analyzed 2 different processes & created the histogram beneath. Yous've as well added the upper control limit and lower command limit of the procedure and the nominal design dimension.
You're Histogram has revealed that process A on the left is evenly centered effectually the Target Specification, just does produce an OOS (Out Of Specification) occasionally. Based on this data yous now know that in order to reduce bit (or OOS), y'all'll demand to eliminate Variation inside your process.
A Histogram of Procedure B reveals that it is NOT centered effectually the Target Specification. In this situation your offset improvement goal would be the Shift the Mean value to the right, so reduce Variation.
This analysis and the Histogram in general, sets the foundation for Process Capability Analysis.
Are You Reliably Meeting the Design Specification
The example in a higher place of the two side-past-side process can also be applied to the Procedure Design Phase of a new product. Similar to improving an existing process, you tin utilize a Histogram to study a make new process in social club to make up one's mind if that process will be acceptable.
Measuring Process Improvements
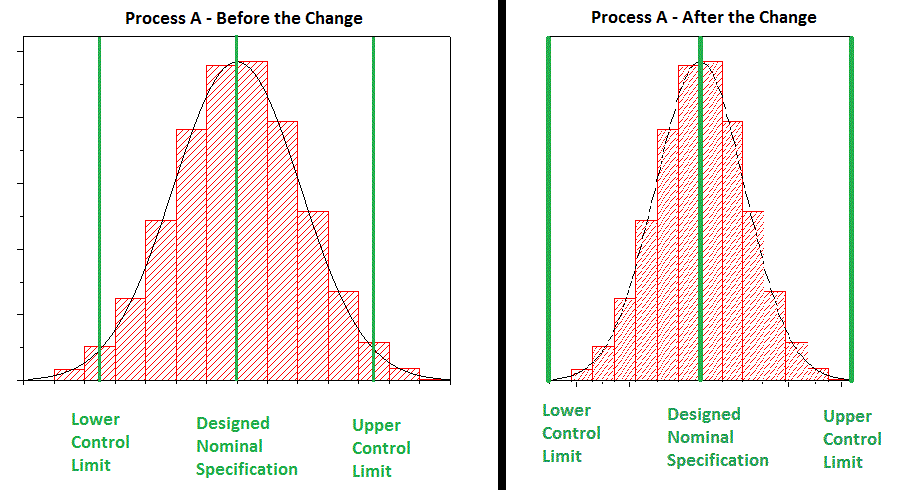
Some other powerful application of the Histogram is to measure if a process improvement was effective.
To continue the example higher up, let'southward say you took your baseline data from Process A and decided that yous needed to eliminate variation. And then you went back to your process and made some adjustments and took a new set of data after the adjustments and saw the following information prepare.
With this piece of assay, you can confirm that your adjustments were successful!
Comparing the Variation of 2 Like Processes
Sometime you'll have two similar processes, perhaps it's two identical assembly lines. These two processes tin be made up of similar pieces of equipment and follow the same process. Practice you expect them to be identical?
You tin employ a Histogram to hands & accurately compare these two processes together. For whatsoever processes that you're analyzing, y'all tin over-lay the resulting Histograms onto the same graph, like to below..
In this style, you can visually compare the Mean, Range, Deviation & Pattern of Variation inside each data fix.
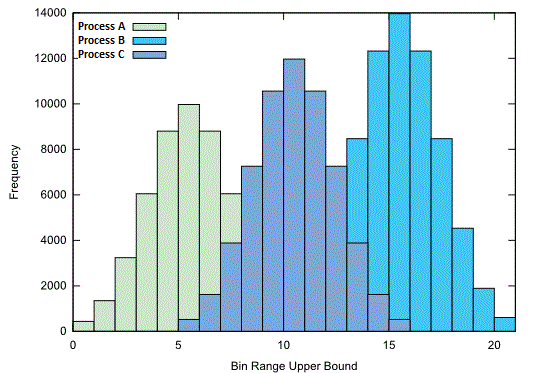
Sometimes when y'all compare 2 data sets together using a Histogram, you may notice that one process has more than data points making it hard to compare the ii processes.
To eliminate this, your information sets should exist "Normalized". By that I mean, split the data in each gear up past information technology's own volume to convert Frequency in Percentage. In doing this, ii data sets can be accurately compared to each other.
Downsides to the Histogram
While the Histogram is a powerful tool, it also has its limitations.
The first downside is the l minimum information points required for adequate assay. This is bad for measurements which are destructive or for products which are built infrequently.
Some other downside is that a Histogram is not powerful enough to let for definitive conclusions regarding small differences in distribution peak locations.
Lastly, the Histogram never reveals the source of the variation. You must pair upwards your histogram with directly observations from your procedure to draw appropriate conclusions about the source of your variation.
External Resources
Shodor Histogram Activity
YouTube How Too Video for Excel 2013
Wikipedia Histogram Page
Quark net.gov histograms
ASQ Histogram Folio
ASQ Histogram Distribution Folio
ASQ Excel Histogram Template
Source: https://cqeacademy.com/cqe-body-of-knowledge/continuous-improvement/quality-control-tools/histograms/
Posted by: vecchionothembeffe.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Read A Histogram -camera"
Post a Comment